Asbestos Exposure - Cause of Mesothelioma
What is Asbestos
Asbestos is a known carcinogen and has been shown to cause not only mesothelioma, but lung cancer, asbestos and other respiratory diseases. Close to 3,000 new cases of mesothelioma are diagnosed each year in the United States.
While the use of asbestos has been curbed in the United States since the late 1970s, the incidence of mesothelioma has been increasing in the United States and worldwide in recent decades.
The risk of developing mesothelioma corresponds to how much asbestos a person was exposed to and how long the asbestos exposure lasted. However, even small amounts of asbestos and infrequent exposure create a risk for contracting mesothelioma or other asbestos-related diseases.
Mesothelioma has an extended latency period and may strike 30 to 50 years after exposure to asbestos. Asbestos was used in many workplaces and in the military, and many victims can trace their exposure to their jobs or military service. Many industries used asbestos, a cheap, durable mineral fiber, in a wide array of building materials, automotive and industrial products, coatings, and insulation materials.
Asbestos Poisoning by Industry
The World Health Organization estimates that asbestos causes approximately half of all deaths from occupational cancer, and 125 million people worldwide are exposed to asbestos in the workplace.
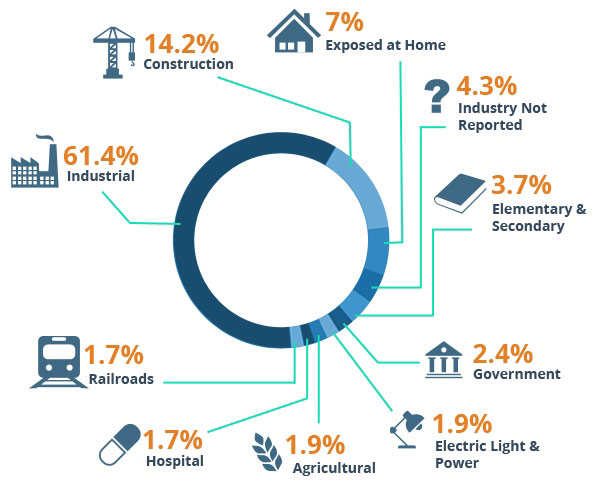
Since there is no safe level of exposure to asbestos, it is important to be aware of asbestos sources and to avoid exposure to all asbestos fibers.

What jobs are the most hazardous for asbestos exposure? What types of workers have the highest risk for Mesothelioma? It is in the handling of asbestos and the breathing of its dust and fibers that constitutes the primary risk-factor for developing an asbestos related pathology, such as mesothelioma. However, even if one hasn’t directly handled the asbestos, one’s risk-factor for asbestos disease still increases if the person has worked in a facility where its dust and fibers are a component of the breathable air.
While many uses for asbestos were banned in the mid-1970’s, the risk from exposure continues to this day because of mesothelioma’s long latency and incubation period. Symptoms, most commonly affecting the lungs, can sometimes take between 10-70 years to appear making diagnosis of the disease difficult. The cancer is highly aggressive and is resistant to many standard cancer treatments.
Today, asbestos continues to be a threat to workers exposed through their occupations and in buildings that were erected or renovated prior to the ban.

Asbestos fibers are so toxic that industrial and trade worker’s families may develop mesothelioma, or another asbestos-related disease, through coming into contact with stray fibers and particles that have built-up on the worker’s clothing, shoes, skin and hair. This type of “second-hand” exposure to asbestos is known as para-occupational exposure is one example of asbestos dangers.
Thousands of workers in a variety of industries have been tragically affected by the dangerous nature of asbestos fibers. However, certain industries, such as the construction and the maritime industries, have a greater occurrence of asbestos-related disease than others do.
Some of the construction trades most at risk from asbestos include (but are not limited to):
- insulators
- plumbers and pipefitters
- electricians
- sheet metal workers
Any construction worker may be in danger during maintenance, remodeling, or demolition of an old building or road.
In addition to asbestos exposure to workers in private industries, sailors, submariners, and other Navy personnel were placed in danger. Shipbuilders were constantly in danger of inhaling asbestos, but those who tore apart old ships so that they may be repaired or refurbished were at an even greater risk.
Unfortunately, many companies were aware of the dangers of asbestos exposure but continued to place their employees at risk. Often called “asbestos cancer,” the prognosis for mesothelioma is grim with the average survival time varying from 4 – 18 months after diagnosis.
Asbestos Injuries
Asbestosis is a noncancerous illness caused by asbestos exposure. The disease occurs when the fibers get lodged in the victim’s lungs, the body tries to protect itself against the fibers which results in the development of scar tissue. In turn, the scar tissue diminishes the lung’s capacity for oxygen. Asbestosis is a progressive disease, and as the lungs’ capacity decreases, victims suffer shortness of breath, coughing, fatigue, chest pain, weight-loss and heart problems. Asbestosis victims may be symptom free and the disease is detected by x-rays.
Asbestosis is a chronic inflammation of the parenchymal tissues of the lungs. The condition occurs after long term exposure to asbestos, usually from working in a mine or other workplaces where asbestos is found. Those who suffer from this condition often have severe shortness of breath, and have a higher risk of developing lung cancer.
The inflammation is due to an immune response in the body, which becomes chronic, and leads to the deposit of fibrous tissues around the asbestos fibers. These fibrous masses eventually start to show symptoms, resulting in shortness of breath and, in rare cases, respiratory failure.
There is currently is no cure for asbestosis, however, the symptoms of the disease can be managed. Treatments for the disease involve preventing further complications of the disease and treating its symptoms. Bronchodilators that open up the bronchial tubes and allow passage of air are used to ease shortness of breath. The patient may also receive supplemental oxygen. Respiratory treatments that remove secretions from the lungs may also be used. Coughing is treated with humidifiers, breathing therapies and chest percussion to loosen and thin bronchial.
Asbestos exposure is also known to cause malignant mesothelioma, a rare, aggressive form of cancer affecting the lining of the lungs that can take up to five decades to be properly diagnosed, and is resistant to many standard cancer treatments.
For more information, please see the following list of Asbestosis information resources:
- Mayo Clinic: Asbestosis
- E-Medicine: Asbestosis
- NIOSH Publications on Asbestos
- About.com: Asbestosis


